Knowledge transfer methods for classification tasks
Mikołaj Małkiński
supervisor: Jacek Mańdziuk
One of the fundamental goals of Artificial Intelligence is to reach levels of a so-called Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), characterized by autonomous learning systems with close to human-level reasoning capabilities. Among many AGI milestones, in the planned research we are particularly interested in intelligent systems that can autonomously (i.e. without external supervision) learn to solve disparate tasks of a given type with efficacy similar to specialized methods, dedicated to the particular tasks. The goal of the conducted research is to create a novel method of constructing universal systems capable of solving disparate classification tasks based on access to unified resources (e.g. joint system architecture or shared memory) and a uniform meta-learning strategy. One of many possibilities of achieving this goal is by employing deep neural networks and task decomposition techniques, which will constitute the central theme of the oncoming research.
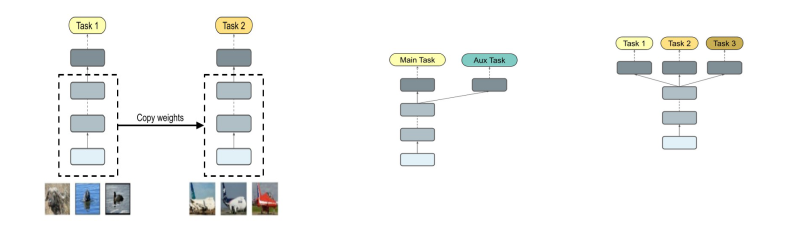
Fig. 1 Examples of knowledge transfer methods. (Left): Inductive transfer learning – a model trained on Task 1 is fine-tuned on Task 2. (Centre): Training with an auxiliary task – a supplementary task is used, which should help the model to discover better features and simplify training. (Right): Multi-task learning – a single model is trained to solve multiple tasks simultaneously.