Computation of nuclear effects in MadGraph5_aMC@NLO at Next-to-Leading order accuracy
Anton Safronov
supervisor: Daniel Kikoła
Automated perturbative computations of cross sections for hard processes (like production of charm and bottom quarks) in asymmetric hadronic/nuclear A+B collisions at the next-to-leading (NLO) order in `α_S` will offer a wide range of applications, such as more robust predictions for new experimental programs, the phenomenology of heavy-ion collisions, and the interpretation of the LHC and RHIC data. Such a goal can be achieved using MadGraph5_aMC@NLO, a well-established tool for automatic generation of matrix elements and event generation for high energy physics processes in elementary collisions, such as decays and `2→n` scatterings.
I have extended the capabilities of MadGraph5_aMC@NLO capabilities by implementing computations for asymmetric collisions, for example `p+Pb`, `π+A`l or `Pb+W` reactions. These new capabilities will soon be made available via the EU Virtual Access NLOAccess (https://nloaccess.in2p3.fr).
I’m going to present the objectives of the NLOAccess initiative, the implementation of asymmetric computation computations in MadGraph5_aMC@NLO along with the computation of the nuclear PDF and scale uncertainties, our cross checks with previous results and codes (FEWZ, MCFM), and predictions for p+Pb collisions at the LHC for charm, bottom and top quark production, as well as fancier observables now made predictable with these new capabilities.
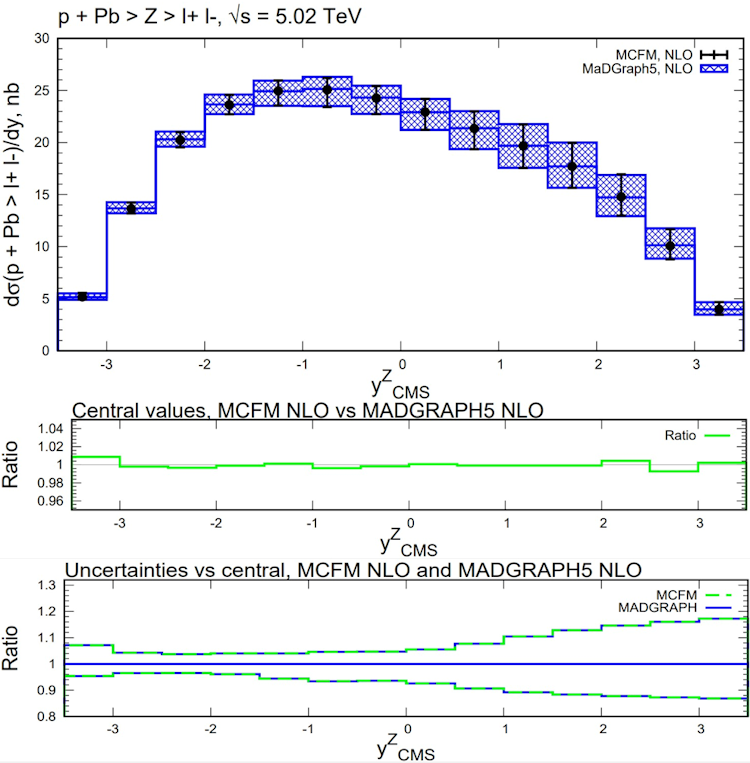
Fig. 1 Comparison of cross section for Z boson production as a function of rapidity in center of mass frame in p-Pb collisions for MG5 and MCFM.