Decomposing bipolar ECG signal using CNN autoencoder
Sebastian Wildowicz
supervisor: Teodor Buchner
This research is aimed at developing new methods of ECG signal analysis, the aim of which is to develop medical diagnostics in the area of cardiology and neuroinformatic. The work concerns the issues of modelling the electrical activity of the heart and the development of techniques for the analyse of the signal source state. The thesis presents an innovative and modern approach for AI solution - CNN autoencoder, which allows decompose and reconstruct bipolar ECG signal from a chosen model of the single base function. Created algorithm is based on the convolution of gaussian curve with single base function. Model consist of: input shape [N x L x K], output shape [N x ADn x 3], 1.360.339 total parameters(trainable parameters: 1.357.299, non-trainable parameters: 3.040)
where: N – number of train datasets, L – number of single ECG lead samples, K – number of bipolar ECG leads, ADn – number of single gaussian curve samples.
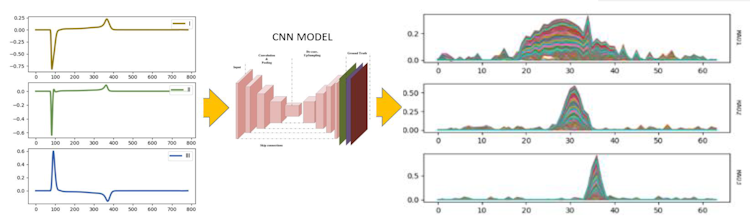
Fig. 1 ECG decompose model
The results of created model presents on Fig. 1 allows to decompose and reconstruct the bipolar ECG signal for the selected base function. Results shows that the ECG signal can be represented by a convolution of gaussian curve with a base function, QRS amplitudes were correctly reconstructed by CNN autoencoder.